A request param is a piece of data that is sent to a web server as part of a HTTP request. Request params can be sent in the URL query string, in the request body, or in request headers.
The most common way to send request params is in the URL query string. The query string is the part of the URL that comes after the question mark (?). For example, the following URL contains a query string:
https://example.com/?name=Bard&age=2 The query string in this example contains two request params: name and age. The value of the name param is Bard and the value of the age param is 2.
Request params can also be sent in the request body. The request body is the part of the HTTP request that contains the data that is being sent to the server. For example, the following POST request contains a request param in the request body:
POST /api/users HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json { "name": "Bard", "age": 2 } The JSON object in the request body contains two request params: name and age. The value of the name param is Bard and the value of the age param is 2.
Request params can also be sent in request headers. Request headers are used to provide additional information about the HTTP request. For example, the following HTTP request contains a request param in the Authorization header:
GET /api/users HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOjIxLCJpYXQiOjE2Njc4MDAwMDB9.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
The Authorization header in this example contains a request param called Bearer. The value of the Bearer param is a JSON Web Token (JWT).
Request params are important because they allow clients to send data to servers. This data can be used by the server to process the request, generate a response, or store the data in a database.
For example, a web application might use request params to allow users to log in, search for products, or add items to their shopping cart.
To use request params, you need to first identify the data that you need to send to the server. Once you have identified the data, you need to choose how you want to send it.
If you are sending a GET request, you can send the request params in the query string. To do this, you need to append the request params to the URL after the question mark (?).
For example, the following URL contains a query string with two request params:
https://example.com/?name=Bard&age=2 If you are sending a POST request, you can send the request params in the request body. To do this, you need to set the Content-Type header to application/json or application/x-www-form-urlencoded. Then, you need to serialize the request params to a JSON object or a form-encoded string.
For example, the following POST request contains a request param in the request body:
POST /api/users HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json { "name": "Bard", "age": 2 } You can also send request params in request headers. To do this, you need to set the name of the request param to the name of the header and the value of the request param to the value of the header.
For example, the following HTTP request contains a request param in the Authorization header:
GET /api/users HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOjIxLCJpYXQiOjE2Njc4MDAwMDB9.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
Here are some best practices for using request params:
- Use descriptive names for your request params. This will make your code more readable and maintainable.
- **Use
WebYou can use the @RequestParam annotation to bind Servlet request parameters (that is, query parameters or form data) to a method argument in a controller. The following. Web@RequestParam makes Spring to map request parameters from the GET/POST request to your method argument. GET Request.. Web9 Answers. @RequestMapping (value = "users/newuser", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String saveUser (@RequestParam Map<String,String> requestParams) throws. WebAug 20, 2020 at 15:43. The reason they have value as an alias for name is that value has a special meaning in annotations. The value annotation parameter is the default, allowed. WebIn Spring MVC, "request parameters" map to query parameters, form data, and parts in multipart requests. This is because the Servlet API combines query parameters and form. WebI know that: @RequestParam takes parameter value whereas @PathVariable takes placeholder value. @RequestParam can be optional (required=false) while making.
PathVariable Vs RequestParam. Difference between PathVariable and RequestParam In Spring Boot
Source: Youtube.com
Spring boot tutorial - @RequestParam annotation with example

Source: Youtube.com
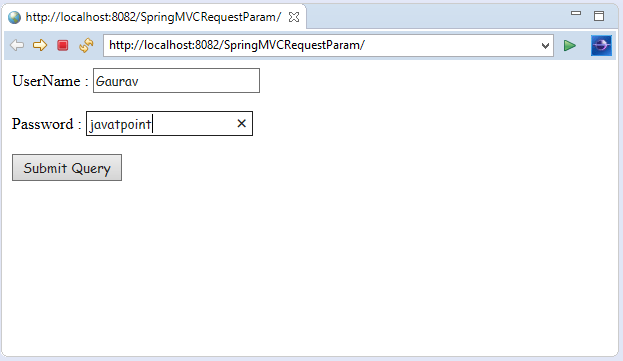
What Is A Request Param, PathVariable Vs RequestParam. Difference between PathVariable and RequestParam In Spring Boot, 8.77 MB, 06:23, 55,744, Infybuzz, 2021-02-09T03:30:01.000000Z, 2, Spring MVC RequestParam Annotation - javatpoint, 361 x 623, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-request-param
What Is A Request Param. Web@PathVariable - must be placed in the endpoint uri and access the query parameter value from the request @RequestParam - must be passed as method.
In this video we will see what is difference between PathVariable and RequestParam in Spring Framework?
As an example here we will see with Spring Boot Application but you can apply same thing for Spring MVC as well. Both the annotations are provide in Spring Framework.
Source Code - infybuzz.com/2019/06/differences-between-requestparam-and.html
Checkout below Courses Provided by me :-
GraphQL with Spring Boot - bit.ly/32E98kc
Build REST API with Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA - bit.ly/2ZUT0JO
Graph Database : Neo4j with Spring Boot - bit.ly/3r63wKc
Jasper Reports with Java & Spring Boot - bit.ly/3mncX5n
Learn MongoDB with Java and Spring Boot using Spring Data MongoDB and MongoRepository. - bit.ly/3a1pNkb
Learn RabbitMQ : Messaging with Java, Spring Boot And Spring MVC - bit.ly/2IRCn9U
Learn Java Messaging Service - Spring MVC, Spring Boot, ActiveMQ - bit.ly/2UdN7V4
Java Interview Preparation || 100+ Quality Questions Covered - bit.ly/33kzLdX
For more GO HERE - infybuzz.com
#java #java8 #infybuzz
What Is A Request Param, WebAug 20, 2020 at 15:43. The reason they have value as an alias for name is that value has a special meaning in annotations. The value annotation parameter is the default, allowed. WebIn Spring MVC, "request parameters" map to query parameters, form data, and parts in multipart requests. This is because the Servlet API combines query parameters and form. WebI know that: @RequestParam takes parameter value whereas @PathVariable takes placeholder value. @RequestParam can be optional (required=false) while making.

Spring MVC RequestParam Annotation - javatpoint - Source: javatpoint.com

Spring - MVC RequestParam Annotation - GeeksforGeeks - Source: geeksforgeeks.org
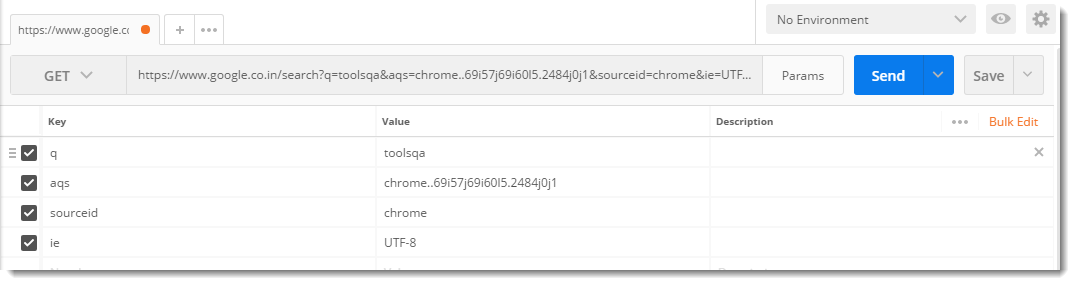
What are Request Parameters in Postman and How to use them? - Source: toolsqa.com
Belum ada tanggapan untuk "What Is A Request Param"
Posting Komentar